Key Takeaways
- Forex brokers act as intermediaries connecting retail traders to the $7.5+ trillion daily forex market through different execution models (Market Maker, ECN, STP)
- Top regulated brokers like IC Markets and Pepperstone offer spreads from 0.0 pips with commissions as low as $3.50 per lot
- Always choose brokers regulated by tier-1 authorities like FCA, ASIC, or CySEC for maximum fund protection
- FCA’s December 2024 regulatory update emphasizes Consumer Duty compliance and stricter oversight of CFD providers
- Test trading platforms via demo accounts—MetaTrader 4/5 and cTrader dominate, but proprietary platforms offer unique advantages
Introduction to Forex Brokers
Think of forex brokers as your gateway to the world’s largest financial market. Just like you need a real estate agent to buy a house, you need a forex broker to trade currencies. But here’s where it gets interesting—not all brokers work the same way, and understanding these differences could mean the difference between profitable trading and costly mistakes.
The forex market sees over $7.5 trillion in daily trading volume according to the latest Bank for International Settlements (BIS) data, making it more liquid than all stock markets combined. Yet most retail traders access this massive market through brokers who might be working against their interests.
Quick Analogy: Forex is like a global farmers’ market—but for currencies. Brokers are like the market organizers who let you rent a stall (trading account) to buy and sell. Some organizers are fair and transparent, others… well, let’s just say they might be peeking at your business plans.
What is a Forex Broker?
A forex broker is a financial services company that provides traders access to a platform for buying and selling foreign currencies. In simple terms, they’re the middleman between you and the massive interbank forex market where banks, hedge funds, and institutions trade billions of dollars every day.
Definition and Role of Forex Brokers
Forex brokers serve several critical functions in the trading ecosystem. They provide the technology infrastructure through trading platforms like MetaTrader 4 or cTrader, execute your trades, and manage the risk associated with your positions. Think of them as your digital trading desk—they handle everything from processing your orders to providing market data and analysis tools.
But here’s what most beginners don’t realize: some brokers make money when you lose, while others profit regardless of your trading outcomes. This fundamental difference shapes everything from the spreads you pay to the execution speed you receive.
How Forex Brokers Act as Intermediaries
When you place a trade through your broker, you’re not directly accessing the interbank market. Instead, your broker either matches your trade with another client, passes it to their liquidity providers (typically large banks), or takes the opposite side of your trade themselves.
This intermediary role is crucial because the interbank market typically requires minimum transaction sizes of $1 million or more. Retail brokers break down these large trades into smaller, accessible portions—allowing you to trade with as little as $100 or even $10 in some cases.
The Forex Market Overview
Understanding the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, or forex, is a decentralized global marketplace where currencies are traded. Unlike stock exchanges that operate from specific locations, forex trading happens electronically over-the-counter (OTC) through a network of banks, financial institutions, and individual traders worldwide.
What makes forex unique is its 24-hour operation cycle. As trading ends in one major financial center, it begins in another—London closes as New York opens, New York hands off to Sydney, and Sydney passes to Tokyo. This continuous cycle creates opportunities but also requires brokers to maintain sophisticated infrastructure across multiple time zones.
Size and Liquidity of the Forex Market
The numbers are staggering. According to 2024 market data, the forex market processes between $6.6 trillion and $8.4 trillion in daily volume. To put this in perspective:
- The United States alone accounts for $1.165 trillion daily (14.1% growth year-over-year)
- Singapore processes $1.085 trillion daily, cementing its role as Asia’s forex hub
- The entire global stock market volume is dwarfed by forex’s daily turnover
Major Players in the Forex Market
The forex ecosystem includes several key participants, each playing a distinct role:
Major Currency Pairs and Cross Pairs
Currency trading revolves around pairs—you’re always buying one currency while selling another. The most liquid pairs, called “majors,” include EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, and USD/CHF. These pairs typically offer the tightest spreads because of their high trading volume and liquidity.
Cross pairs (like EUR/GBP or AUD/JPY) exclude the US dollar and often have wider spreads. Exotic pairs, featuring emerging market currencies, can have spreads of 10+ pips and require careful broker selection.
Market Participants
Understanding who trades forex helps explain how brokers fit into the ecosystem:
- Central Banks: Control monetary policy and can move markets with single announcements
- Commercial Banks: Provide liquidity to brokers and handle corporate forex needs
- Hedge Funds & Institutions: Drive major market movements with large-scale trades
- Corporations: Trade forex for business operations, not speculation
- Retail Traders: Individual traders accessing markets through brokers
Types of Forex Brokers
Not all brokers are created equal. Understanding the three main broker types is crucial because it affects everything from your trading costs to execution speed. Let me break down each type with real-world examples.
Market Makers vs. ECN vs. STP Brokers
Market Makers (Dealing Desk Brokers)
Market makers create their own market for your trades. When you buy EUR/USD, they might take the opposite side—essentially betting against you. This isn’t necessarily bad, but it creates a potential conflict of interest.
How They Work: Market makers quote their own bid and ask prices, often adding a markup to interbank spreads. They profit from spreads and, controversially, when traders lose money. Many retail brokers operate this model because it’s highly profitable.
Advantages:
- Fixed spreads (predictable costs)
- Instant execution (no waiting for market matching)
- Lower minimum deposits
- No commission fees (profit comes from spreads)
Disadvantages:
- Potential conflict of interest (broker profits when you lose)
- Wider spreads than ECN brokers
- Possible price manipulation during high volatility
- Limited transparency in trade execution
ECN Brokers (Electronic Communications Network)
ECN brokers provide direct access to the interbank market through an electronic network. Your trades are matched with other participants—banks, hedge funds, or other traders—at the best available prices.
Real Example: IC Markets operates as a true ECN broker, offering spreads from 0.0 pips on EUR/USD with commissions starting at $3.50 per lot.
Open Your IC Markets AccountHow They Work: ECN brokers aggregate prices from multiple liquidity providers and display the best bid/ask prices. They earn money through commissions, not spreads, aligning their interests with yours.
Advantages:
- Transparent pricing with market depth
- Ultra-tight spreads (often 0.0 pips)
- No conflict of interest
- Fast execution speeds
- Ability to see market depth (Level II pricing)
Disadvantages:
- Commission fees on every trade
- Variable spreads (can widen during volatility)
- Higher minimum deposits required
- More complex pricing structure
STP Brokers (Straight Through Processing)
STP brokers automatically route your trades to liquidity providers without manual intervention. They’re like ECN brokers but without the electronic network—instead, they have direct relationships with banks and other institutions.
Real Example: Pepperstone uses STP execution with access to over 20 liquidity providers, offering raw spreads from 0.0 pips plus commissions.
Open Your Pepperstone AccountHybrid Brokers
Many modern brokers combine multiple execution models. They might use STP for professional accounts and market making for standard retail accounts. This flexibility allows them to serve different client types effectively.
| Broker Type | Execution Model | Typical Spreads | Commissions | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Market Maker | Internal matching | 1-3 pips (fixed) | None | Beginners |
| ECN | Electronic network | 0.0-0.5 pips | $3-7 per lot | Active traders |
| STP | Direct to liquidity | 0.1-1.0 pips | Variable | Intermediate traders |
How Do Forex Brokers Facilitate Trades?
Ever wondered what happens in the milliseconds between clicking “Buy” and seeing your position open? The trade facilitation process involves sophisticated technology, risk management, and financial engineering that most traders never see.
The Mechanics of Forex Trading
Currency Pairs and Bid-Ask Spreads
Every forex quote shows two prices: the bid (what buyers are willing to pay) and the ask (what sellers are asking). The difference is the spread—essentially the broker’s markup on each trade.
For example, if EUR/USD shows 1.0850/1.0852, the spread is 2 pips. On a standard lot (100,000 units), this 2-pip spread costs you about $20. Multiply this across thousands of trades, and you’ll understand why spread comparison is crucial when choosing a broker.
Think of it like this: Spreads are like the bid-ask spread on a used car. The dealer buys at $10,000 (bid) and sells at $10,500 (ask). The $500 difference is their profit margin—same concept in forex.
How Forex Brokers Handle Orders
When you place an order, several things happen simultaneously:
- Order Validation: The broker checks your account balance, available margin, and position limits
- Risk Assessment: Automated systems evaluate the trade’s impact on the broker’s overall risk exposure
- Price Discovery: The broker determines the best available price based on their execution model
- Execution: The trade is either internally matched, sent to liquidity providers, or taken on the broker’s book
- Confirmation: You receive trade confirmation and position updates
This entire process typically takes 50-200 milliseconds for top-tier brokers. BlackBull Markets leads execution speed rankings with ~50ms for limit orders.
Order Execution Models
Market Execution
Market execution means your order gets filled at the best available price when it reaches the market. There’s no price guarantee—if the market moves between order placement and execution, you might get a different price than expected (called slippage).
This model is common with ECN and STP brokers because they’re passing your orders to real market participants. The advantage is faster execution and no requotes; the downside is potential slippage during volatile periods.
Instant Execution
Instant execution guarantees the price you see when placing the order—or the broker rejects your order entirely. Market makers typically use this model because they control their own prices.
While you get price certainty, instant execution can lead to requotes during fast markets. If prices move unfavorably while your order is being processed, the broker might offer you a worse price or reject the trade entirely.
Request for Quote (RFQ)
RFQ execution requires the broker to provide a quote before you can trade. This model is rare in retail forex but common for large transactions or exotic currency pairs where liquidity is limited.
The Importance of Liquidity Providers
Behind every good broker is a network of liquidity providers—the banks and institutions that actually have the money to trade currencies in massive volumes.
Role of Banks and Financial Institutions
Tier-1 banks like JPMorgan, Citibank, and Deutsche Bank form the backbone of forex liquidity. These institutions trade directly with each other in the interbank market, creating the prices that eventually reach retail traders.
Top brokers typically have relationships with 10-20+ liquidity providers. Pepperstone, for instance, aggregates prices from over 20 banks and institutions to offer competitive spreads.
Order Matching Mechanisms
Modern brokers use sophisticated algorithms to match and route orders:
- Price Aggregation: Combining quotes from multiple sources to find the best price
- Smart Order Routing: Automatically sending orders to the provider offering the best execution
- Latency Optimization: Using co-location and direct market access to minimize delays
- Risk Management: Hedging broker exposure through dynamic position management
How Do Forex Brokers Make Money?
Understanding how your broker makes money is crucial—it reveals potential conflicts of interest and helps you choose brokers whose incentives align with your success. Let’s break down the main revenue streams.
Spreads and Commissions
Understanding Spreads in Forex Trading
Spreads are the most common way brokers generate revenue. They either markup the raw interbank spread or charge the raw spread plus a commission. Here’s how the numbers work with real broker examples:
| Broker | Account Type | EUR/USD Spread | Commission per Lot | Total Cost (1 lot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC Markets | Raw Spread | 0.02 pips | $3.50 | $3.52 |
| Pepperstone | Razor | 0.10 pips | $3.50 | $4.50 |
| XM | Standard | 0.8 pips | $0 | $8.00 |
| Exness | Pro | 0.0 pips | $3.50 | $3.50 |
Notice how IC Markets and Exness offer the lowest total trading costs? This is why professional traders prefer ECN brokers—the transparent pricing model often results in lower overall costs.
Open Your Exness AccountFixed vs. Variable Spreads
Fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions. Market makers typically offer fixed spreads because they control pricing. Variable spreads fluctuate based on market liquidity and volatility—they can be as low as 0.0 pips during quiet periods but widen to 5+ pips during major news events.
Here’s the trade-off: Fixed spreads offer predictability but are usually wider than average variable spreads. Variable spreads can be incredibly tight but might widen when you least expect it.
Additional Revenue Streams
Overnight Swap Fees (Rollover Fees)
When you hold positions overnight, brokers charge or pay you swap fees based on interest rate differentials between the currencies in your pair. This seemingly small fee can add up significantly for long-term positions.
For example, if you’re long EUR/USD and the EUR interest rate is lower than USD, you’ll pay a negative swap. Conversely, if you’re long a high-yielding currency against a low-yielding one, you might earn positive swap.
Inactivity and Withdrawal Fees
Many brokers charge inactivity fees (typically $10-50 per month) if you don’t trade for extended periods. Withdrawal fees vary widely—some brokers like IC Markets offer free withdrawals, while others charge $20-40 per withdrawal.
The Dark Side: Conflict of Interest with Market Makers
Here’s what most brokers won’t tell you: Market makers profit when you lose money. If 80% of retail traders lose money (and they do), market makers can simply take the opposite side of all trades and profit from the statistical edge.
This creates several concerning practices:
- Price Manipulation: Slightly adjusting prices to trigger stop losses
- Requotes: Delaying execution when trades would be profitable for clients
- Spread Widening: Increasing spreads during volatile periods to reduce client profits
- Platform Issues: Mysterious connection problems during profitable trades
Regulatory Protection: The FCA’s December 2024 update specifically addresses these issues, requiring brokers to demonstrate fair pricing and transparent execution. Always choose regulated brokers to minimize these risks.
Regulation and Security in Forex Trading
Regulation isn’t just bureaucratic red tape—it’s your financial lifeline. The difference between regulated and unregulated brokers can mean the difference between getting your money back or losing everything to fraud.
Why Forex Broker Regulation Is Important
Regulated brokers must follow strict rules designed to protect your interests. These include segregating client funds, maintaining adequate capital reserves, and submitting to regular audits. But not all regulations are created equal.
Protecting Traders from Fraud
Horror stories of broker fraud are common in unregulated jurisdictions. Clients wake up to find their accounts frozen, withdrawals blocked, or entire companies vanished overnight. Regulation provides legal recourse and, in many cases, compensation schemes.
Major Regulatory Authorities
Tier-1 Regulators (Strongest Protection)
Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) – United Kingdom: Considered the gold standard of forex regulation. FCA-regulated brokers must segregate client funds, provide negative balance protection, and contribute to the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS), which covers up to £85,000 per client.
The FCA’s December 2024 portfolio letter outlines seven key priorities for CFD providers, including enhanced Consumer Duty requirements and stricter oversight of client asset protection.
Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC): ASIC-regulated brokers offer excellent protection with segregated accounts and compensation schemes. Unlike ESMA, ASIC doesn’t impose leverage caps, allowing up to 1:500 leverage for experienced traders.
Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) & National Futures Association (NFA) – United States: The most restrictive but protective regime. US brokers must maintain massive capital reserves and offer SIPC insurance, but leverage is capped at 50:1 for major pairs.
Tier-2 Regulators (Good Protection)
Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC): Popular among EU brokers due to passporting rights. CySEC follows ESMA guidelines, including 30:1 leverage caps for retail clients and negative balance protection.
Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS): Strict Asian regulator with strong capital requirements and sophisticated oversight.
Current Regulatory Updates (2024-2025)
| Regulator | Leverage Limits | Segregation Required | Compensation Scheme | Recent Updates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCA (UK) | 30:1 (majors) | Yes | £85,000 (FSCS) | Consumer Duty emphasis |
| ASIC (AU) | 30:1 (retail) | Yes | AU$250,000 | Foreign reporting rules |
| CySEC (CY) | 30:1 (majors) | Yes | €20,000 (ICF) | Fractional CFD rules |
| CFTC/NFA (US) | 50:1 (majors) | Yes | $250,000 (SIPC) | Stable regulations |
How Regulated Brokers Protect Traders
Segregated Client Funds
Regulated brokers must keep your money separate from their operational funds. This means even if the broker goes bankrupt, your money remains protected and can be returned to clients.
Here’s how top brokers implement segregation:
- IC Markets: Client funds held with National Australia Bank in segregated accounts
- Pepperstone: Tier-1 bank segregation across multiple jurisdictions
- FXTM: Segregated accounts with Barclays Bank and other major institutions
Negative Balance Protection
This crucial protection ensures you cannot lose more than your account balance, even during extreme market volatility. It became standard after the 2015 Swiss franc shock wiped out many client accounts.
ESMA made negative balance protection mandatory for EU retail clients in 2018, and most reputable brokers now offer it globally as a competitive advantage.
Top Regulated Forex Brokers: Detailed Analysis
Based on our research of the top-ranking brokers and 2025 industry awards, here are the standout performers that consistently deliver excellent service to traders worldwide.
IC Markets – Best Overall Spreads

Regulation: ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), FSA (Seychelles)
Founded: 2007 | Headquarters: Sydney, Australia
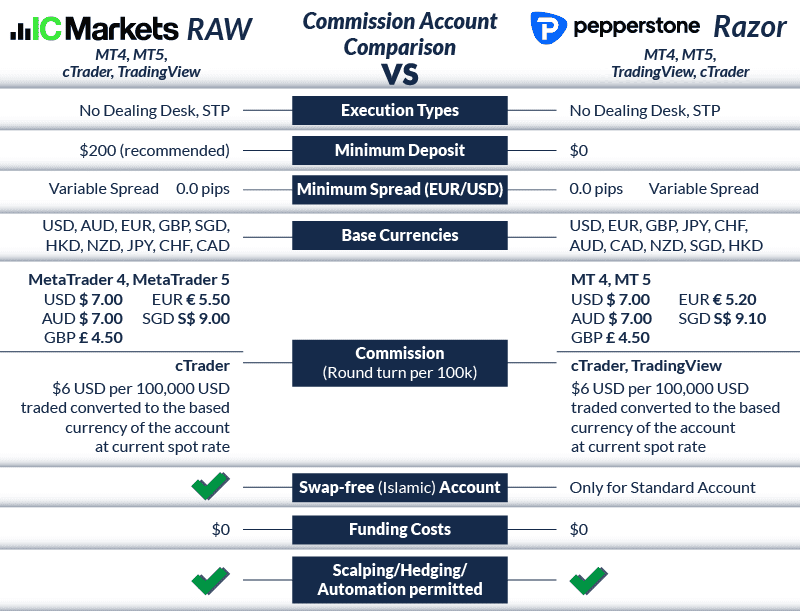
IC Markets dominates the low-spread category with industry-leading pricing. Their Raw Spread account offers EUR/USD from just 0.02 pips plus $3.50 USD commission per lot—making them the cheapest option for active traders.
Key Features:
- True ECN execution with market depth visibility
- Ultra-fast execution (sub-50ms average)
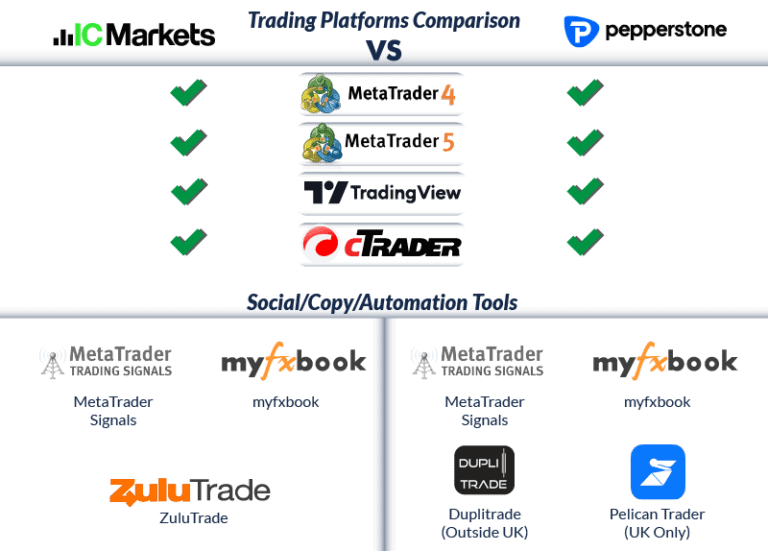
- MetaTrader 4/5, cTrader, and proprietary platforms
- Over 232 tradeable instruments
- No minimum deposit on standard accounts
Trading Costs (Raw Spread Account):
| Currency Pair | Average Spread | Commission | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | 0.02 pips | $3.50 | $3.52 |
| GBP/USD | 0.23 pips | $3.50 | $5.80 |
| AUD/USD | 0.03 pips | $3.50 | $3.80 |
Pepperstone – Best Trading Technology
Regulation: FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia), DFSA (Dubai), CySEC (Cyprus), BaFin (Germany)
Founded: 2010 | Headquarters: Melbourne, Australia
Pepperstone wins on technology and regulation—they’re licensed in seven jurisdictions and offer cutting-edge trading tools. Their Smart Trader Tools for MT4 and TradingView integration set them apart from competitors.
Key Features:
- Seven-tier regulatory coverage including FCA and BaFin
- Smart Trader Tools with 10 advanced features
- Capitalise AI for automated trading
- Raw spreads from 0.0 pips + $3.50 commission
- 24/7 multilingual support
Platform Options:
- MetaTrader 4 with Smart Trader Tools enhancement
- MetaTrader 5 with advanced charting
- cTrader for professional traders
- TradingView integration
- Pepperstone mobile app
FXTM – Best All-Around Broker
Regulation: FCA (UK), CySEC (Cyprus), FSCA (South Africa)
Founded: 2011 | Headquarters: Cyprus
FXTM combines competitive pricing with excellent educational resources and strong regulation. They’re particularly popular among intermediate traders who want reliable execution without premium pricing.
Why Traders Choose FXTM:
- Comprehensive education through FXTM Academy
- Regular market analysis and trading webinars
- Multiple account types for different experience levels
- Copy trading and social trading features
- Strong regulatory oversight across three jurisdictions
Exness – Best for High Leverage
Regulation: CySEC (Cyprus), FCA (UK), FSA (Seychelles), FSCA (South Africa)
Founded: 2008 | Headquarters: Cyprus
Exness offers unlimited leverage for experienced traders while maintaining tight spreads and instant withdrawals. Their Pro account delivers 0.0 pip spreads on major pairs.
Standout Features:
- Unlimited leverage available (after qualification)
- Instant withdrawal processing
- 0.0 pip spreads on Pro accounts
- No minimum deposit requirement
- Advanced risk management tools
Tickmill – Best for Low-Volume Traders
Regulation: FCA (UK), CySEC (Cyprus), FSCA (South Africa), FSA (Seychelles)
Founded: 2014 | Headquarters: UK
Tickmill offers some of the lowest minimum deposits and trading requirements, making them ideal for beginners and small-account traders who still want professional-grade execution.
Open Your Tickmill AccountEightcap – Best for Education
Regulation: ASIC (Australia), FCA (UK), CySEC (Cyprus)
Founded: 2009 | Headquarters: Melbourne, Australia
Eightcap combines competitive spreads (from 0.1 pips) with comprehensive educational resources. Their AI-powered economic calendar and Flash Trader for MT5 provide excellent value for developing traders.
Open Your Eightcap AccountHow to Choose the Right Forex Broker
Choosing a forex broker is like choosing a business partner—you want someone reliable, cost-effective, and aligned with your goals. Here’s a systematic approach to making the right choice.
The 5-Point Broker Selection Framework
1. Regulatory Compliance (Non-Negotiable)
Never compromise on regulation. Your broker should be licensed by at least one tier-1 authority (FCA, ASIC, CFTC/NFA) or tier-2 regulator (CySEC, MAS). Check the regulator’s website to verify the license—don’t trust the broker’s claims alone.
Red Flags:
- Unregulated or offshore-only regulation
- Claims of regulation without license numbers
- Recent regulatory warnings or sanctions
- Pressure to deposit before verification
2. Trading Costs Analysis
Calculate your total trading costs including spreads, commissions, and swap fees. Use this formula for commission-based accounts:
Total Cost = (Spread in pips × $10) + Commission per lot
For example, IC Markets’ EUR/USD trade costs: (0.02 × $10) + $3.50 = $3.70 per lot
3. Platform and Technology
Your platform is your trading lifeline. Consider these factors:
- Stability: No disconnections during volatile markets
- Speed: Fast order execution (under 100ms)
- Features: Charting tools, indicators, automated trading support
- Mobile Access: Full-featured mobile apps
- Customization: Ability to modify interface and tools
4. Customer Support Quality
Test support before you need it. Contact potential brokers with questions and evaluate their response time and helpfulness. Quality brokers offer 24/5 support (24 hours during market days) in multiple languages.
5. Account Types and Flexibility
Different account types serve different trading styles:
| Account Type | Best For | Typical Features | Minimum Deposit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard/Retail | Beginners | Fixed spreads, no commission | $100-500 |
| ECN/Raw | Active traders | Raw spreads + commission | $500-1,000 |
| Professional | Experienced traders | Higher leverage, lower costs | $10,000+ |
| Islamic/Swap-Free | Muslim traders | No overnight interest | Varies |
Due Diligence Checklist
Before opening an account, verify:
- ✅ Regulatory license (check regulator’s website)
- ✅ Segregated fund protection
- ✅ Compensation scheme coverage
- ✅ Transparent fee structure
- ✅ Demo account availability
- ✅ Withdrawal policy and fees
- ✅ Platform stability (test demo first)
- ✅ Customer support responsiveness
- ✅ Online reviews and reputation
- ✅ Financial stability (public companies preferred)
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Chasing Bonuses Over Fundamentals
High deposit bonuses often come with restrictive terms. A $500 bonus might require 50 standard lots of trading before withdrawal—potentially costing more in spreads than the bonus is worth.
Ignoring the Fine Print
Always read terms and conditions, especially regarding:
- Withdrawal restrictions and fees
- Inactivity charges
- Swap/rollover calculations
- Platform downtime policies
- Account closure procedures
Choosing Based on Leverage Alone
High leverage is dangerous for inexperienced traders. A 1:500 leverage means you can control $50,000 with just $100—but you can also lose everything with a 0.2% adverse move.
Forex Trading Platforms: MetaTrader vs. cTrader vs. Proprietary
Your trading platform is your window to the markets. The right platform can enhance your trading, while the wrong one can cost you money through poor execution or missing features.
MetaTrader 4 & 5: Industry Standards
MetaTrader platforms power over 70% of retail forex trading. MT4 focuses on forex and CFDs, while MT5 offers more asset classes and advanced features.
MetaTrader 4 Advantages:
- Vast library of custom indicators and Expert Advisors
- Simple, intuitive interface
- Excellent for automated trading
- Universal broker support
- Strong community and educational resources
MetaTrader 5 Improvements:
- More timeframes (21 vs. 9 in MT4)
- Advanced order types
- Economic calendar integration
- Better backtesting capabilities
- More technical indicators (38 vs. 30)
cTrader: The Professional’s Choice
cTrader offers more advanced features and better transparency than MetaTrader. It’s particularly popular among scalpers and professional traders who need level II pricing and fast execution.
cTrader Advantages:
- Level II market depth (see actual market orders)
- One-click trading with risk management
- Advanced charting with more drawing tools
- Better position and order management
- Transparent ECN execution
cTrader Limitations:
- Fewer brokers offer cTrader
- Smaller community and fewer custom indicators
- Steeper learning curve for beginners
Proprietary Platforms: Broker-Specific Solutions
Many brokers develop their own platforms to differentiate their services. These can offer unique features but often lack the third-party tool ecosystem of MetaTrader or cTrader.
Examples of Successful Proprietary Platforms:
- IG’s Platform: Integrated news, analysis, and advanced charting
- OANDA’s fxTrade: Fractional pip pricing and position-level P&L
- Plus500’s WebTrader: Simple interface optimized for CFD trading
Mobile Trading: Essential for Modern Traders
Mobile trading isn’t just convenient—it’s essential for managing positions and reacting to market news. The best mobile apps offer:
- Full charting capabilities with technical indicators
- One-touch order placement and modification
- Push notifications for price alerts and margin calls
- Integrated news and economic calendar
- Account management features
Risk Management Tools and Features
The best broker in the world won’t save you from poor risk management. However, brokers do provide tools that can help you manage risk more effectively. Here’s what to look for.
Essential Risk Management Features
Stop Loss and Take Profit Orders
Basic stop loss and take profit orders should be available on all platforms. More advanced brokers offer trailing stops that move with favorable price action, protecting profits while allowing for further gains.
Guaranteed Stop Loss
Regular stop losses can suffer from slippage during volatile markets. Guaranteed stop losses ensure execution at your specified price, though brokers typically charge a premium for this protection.
Brokers Offering Guaranteed Stops:
- IG Group (premium charged)
- City Index (fee-based)
- OANDA (selected instruments)
Negative Balance Protection
This ensures you can’t lose more than your account balance, even during extreme market events like the 2015 Swiss franc shock. It’s mandatory for EU retail clients and offered voluntarily by most reputable brokers worldwide.
Advanced Risk Management Tools
Position Sizing Calculators
Good brokers provide position sizing tools that calculate appropriate lot sizes based on your account balance, risk tolerance, and stop loss distance. This prevents over-leveraging and account blowouts.
Margin Level Monitoring
Real-time margin level displays help you understand how close you are to a margin call. Quality platforms show:
- Current margin level percentage
- Free margin available for new positions
- Margin call and stop out levels
- Visual warnings as margin decreases
Economic Calendar Integration
High-impact news can cause significant price movements. The best brokers integrate economic calendars directly into their platforms, allowing you to:
- See upcoming news events by impact level
- Set alerts for specific announcements
- Adjust position sizes before volatile periods
- Close positions before major news if desired
The Future of Forex Brokerage
The forex brokerage industry is evolving rapidly, driven by technology advances, regulatory changes, and shifting trader expectations. Understanding these trends helps you choose brokers positioned for long-term success.
Technological Advancements
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI is transforming forex trading through:
- Automated Analysis: AI-powered market analysis and trade suggestions
- Risk Management: Dynamic risk assessment and position sizing
- Execution Optimization: Smart order routing and slippage minimization
- Fraud Detection: Advanced algorithms detecting suspicious trading patterns
Brokers like Pepperstone are already integrating AI through their Capitalise AI platform, allowing code-free automated trading strategies.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Integration
Leading brokers are integrating cryptocurrency trading alongside traditional forex. This includes:
- Crypto-to-fiat pairs (BTC/USD, ETH/EUR)
- Blockchain-based settlement systems
- Cryptocurrency funding and withdrawal options
- DeFi integration for yield-generating deposits
Regulatory Evolution
Regulations continue tightening globally, with focus on:
- Enhanced Disclosure: More transparent fee structures and risk warnings
- Behavioral Analysis: Monitoring for problem gambling-like trading behavior
- Technology Standards: Minimum requirements for platform stability and security
- Cross-Border Cooperation: Better coordination between international regulators
2024-2025 Regulatory Focus: The FCA’s latest guidance emphasizes Consumer Duty implementation, suggesting stricter requirements for demonstrating positive client outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the differences between market makers and ECN brokers?
- Market makers create their own prices and may take the opposite side of your trades, while ECN brokers connect you directly to the interbank market with transparent pricing. ECN brokers typically offer tighter spreads plus commissions, while market makers offer wider spreads with no commission.
- How do forex brokers provide leverage?
- Brokers provide leverage by lending you money to control larger positions than your account balance would normally allow. For example, 100:1 leverage means you can control $100,000 with just $1,000 in margin. The broker covers the remaining $99,000 temporarily.
- Can forex brokers manipulate market prices?
- Market maker brokers can adjust their own prices within reason, but regulated brokers face strict oversight. ECN and STP brokers cannot manipulate prices as they pass trades directly to the interbank market. This is why regulation and broker type selection are crucial.
- What are the risks of trading with an unregulated broker?
- Unregulated brokers may engage in price manipulation, refuse withdrawals, lack segregated funds, or disappear entirely with client money. You have no legal recourse or compensation schemes with unregulated brokers. Always choose brokers regulated by recognized authorities.
- How are forex brokers regulated?
- Forex brokers are regulated by financial authorities in their operating jurisdictions. Key regulators include FCA (UK), ASIC (Australia), CySEC (Cyprus), and CFTC/NFA (USA). Regulators enforce capital requirements, fund segregation, fair dealing, and provide compensation schemes.
- What is the spread in forex trading?
- The spread is the difference between the bid price (what buyers pay) and ask price (what sellers receive). It’s typically measured in pips and represents the broker’s markup. EUR/USD with a 1.2-pip spread means you pay 1.2 pips above the mid-market price to buy.
- How do I open an account with a forex broker?
- Account opening typically requires: 1) Online application with personal details, 2) Identity verification (passport/license), 3) Address proof (utility bill), 4) Risk assessment questionnaire, 5) Initial deposit. The process usually takes 1-3 business days for regulated brokers.
- What fees should I expect from a forex broker?
- Common fees include spreads (0.1-3 pips), commissions ($3-7 per lot for ECN accounts), swap/rollover fees for overnight positions, withdrawal fees ($0-40), and potential inactivity fees ($10-50 monthly). Always check the complete fee schedule before opening an account.
- How do forex brokers handle client funds?
- Regulated brokers must segregate client funds from their operational money in separate bank accounts. This ensures your money remains protected even if the broker faces financial difficulties. Top-tier banks like Barclays or National Australia Bank typically hold these segregated funds.
- What is a demo account in forex trading?
- Demo accounts let you practice trading with virtual money in real market conditions. They’re essential for testing platforms, strategies, and broker execution quality. Most brokers offer unlimited demo access, though some expire after 30-90 days of inactivity.
- How does leverage affect my forex trades?
- Leverage amplifies both profits and losses. With 100:1 leverage, a 1% favorable move generates 100% profit, but a 1% adverse move wipes out your account. Higher leverage requires smaller margin deposits but dramatically increases risk. EU retail clients are limited to 30:1 leverage on major pairs.
- What is a margin call in forex trading?
- A margin call occurs when your account equity falls below the required margin level (typically 100%). The broker may close your positions automatically to prevent further losses. Some brokers issue warnings at 120-150% margin levels, giving you time to add funds or close positions.
- Can I trade forex without a broker?
- Retail traders cannot access the interbank forex market directly due to minimum transaction sizes ($1+ million) and credit requirements. Banks and large institutions trade directly, but individuals must use brokers or market makers to access forex markets with smaller capital.
- What are swap rates or rollover fees?
- Swap rates are interest payments or charges for holding positions overnight. They’re based on interest rate differentials between the currencies in your pair. If you’re long a high-yielding currency against a low-yielding one, you may earn positive swap. Otherwise, you’ll pay a fee.
- What happens if my broker goes bankrupt?
- With regulated brokers, your funds should be protected through segregation and compensation schemes. FCA-regulated brokers offer up to £85,000 FSCS protection, while ASIC brokers provide AU$250,000 coverage. Unregulated brokers offer no such protection, and you may lose everything.
- How does regulation impact my trading safety?
- Regulation ensures fund segregation, fair pricing, adequate capital reserves, and provides legal recourse. Regulated brokers undergo regular audits and must comply with strict operational standards. They also contribute to compensation schemes that protect clients if the broker fails.
- What should I look for in a forex trading platform?
- Key platform features include stability (no disconnections), fast execution speeds (<100ms), comprehensive charting tools, automated trading support, mobile access, real-time news integration, and easy order management. Test platforms thoroughly using demo accounts before committing real money.
- Can I trade forex 24/7?
- Forex markets operate 24 hours Monday through Friday, from Sydney open (Sunday 5 PM EST) to New York close (Friday 5 PM EST). However, liquidity and spreads vary significantly—the best trading conditions typically occur during London-New York overlap (8 AM – 12 PM EST).
- What is the best type of forex broker for beginners?
- Beginners should prioritize regulation, education, and support over raw spreads. Look for FCA or ASIC-regulated brokers offering comprehensive educational resources, demo accounts, responsive customer support, and simple platform interfaces. Avoid high leverage until you gain experience.
- What is slippage, and how does it affect trading?
- Slippage occurs when your order executes at a different price than requested, typically during high volatility or low liquidity. Positive slippage helps you (better price), while negative slippage increases costs. ECN brokers typically experience less slippage than market makers due to direct market access.
- How do brokers handle losing trades?
- This depends on the broker type. Market makers may profit from losing trades since they take the opposite side. ECN/STP brokers simply earn commissions regardless of trade outcomes. Quality brokers never interfere with individual trades, focusing instead on providing fair execution and competitive pricing.
- Can I lose more money than I deposit with a forex broker?
- With negative balance protection (standard for EU retail clients), you cannot lose more than your account balance. However, without this protection, extreme market moves could theoretically create negative balances. Professional traders and those outside protective jurisdictions face this risk.
- What is the minimum deposit required to start forex trading?
- Minimum deposits vary widely: $1-10 for some brokers, $100-500 for standard accounts, and $1,000+ for premium ECN accounts. However, starting with at least $1,000 is recommended to maintain proper risk management (risking 1-2% per trade).
- How do I know if a forex broker is reliable?
- Check regulation status on the regulator’s official website, verify segregated fund protection, read independent reviews, test customer support responsiveness, examine the fee structure for transparency, and ensure they offer demo accounts for testing. Avoid brokers with regulatory warnings or suspicious practices.
- How do forex brokers handle slippage?
- Reputable brokers minimize slippage through fast execution systems and quality liquidity providers. ECN brokers typically offer better slippage statistics due to direct market access. Some brokers provide slippage statistics in their execution reports, while others offer price improvement when beneficial to clients.
- Are forex brokers regulated in all countries?
- No, regulatory standards vary significantly worldwide. Some countries have strong oversight (UK, Australia, USA), others have developing frameworks (many emerging markets), and some offer minimal regulation (offshore jurisdictions). Always verify specific regulatory status rather than assuming protection.
- What is the typical spread for major currency pairs?
- Raw spreads from top ECN brokers: EUR/USD 0.0-0.2 pips, GBP/USD 0.2-0.5 pips, USD/JPY 0.1-0.3 pips. Standard accounts typically add 0.8-1.5 pips markup. Market makers offer fixed spreads of 1-3 pips. Spreads widen during low liquidity periods and major news events.
- Can I have multiple accounts with different forex brokers?
- Yes, many professional traders use multiple brokers to diversify risk, access different markets, compare execution quality, or take advantage of specific features. However, ensure you can adequately manage and fund multiple accounts while maintaining proper risk management across all positions.
- How do forex brokers handle high-impact news events?
- During major news releases, brokers may widen spreads, increase margin requirements, or temporarily disable trading in affected pairs. Quality brokers communicate these restrictions in advance and maintain orderly markets. Some offer “news trading” accounts with enhanced margin and execution features.
- What is the average leverage offered by forex brokers?
- Leverage limits depend on regulation: EU retail clients are capped at 30:1 for majors, US traders at 50:1, while offshore brokers may offer 500:1 or higher. ASIC allows up to 30:1 for retail clients but higher leverage for wholesale clients. Professional trader classifications may access higher leverage.
- Are there any hidden fees when trading with forex brokers?
- Reputable brokers disclose all fees transparently. Potential “hidden” costs include: weekend holding fees, currency conversion charges, data feed subscriptions, withdrawal fees for small amounts, and inactivity fees. Always read the complete fee schedule and terms of service before opening an account.
Conclusion
Key Points to Remember When Choosing a Forex Broker
Choosing the right forex broker is one of the most important decisions you’ll make as a trader. Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored how brokers operate, their various business models, and the critical factors that separate excellent brokers from mediocre ones.
The forex market’s massive $7.5+ trillion daily volume offers incredible opportunities, but accessing this market safely requires a reliable, regulated intermediary. Whether you choose an ECN broker like IC Markets for ultra-low spreads, or a well-rounded option like Pepperstone for superior technology, your broker choice will significantly impact your trading success.
The Importance of Regulation
Never compromise on regulation. The FCA’s December 2024 updates demonstrate regulators’ ongoing commitment to protecting retail traders through enhanced Consumer Duty requirements and stricter oversight. Choosing brokers regulated by tier-1 authorities like the FCA, ASIC, or CySEC provides essential protections including segregated funds, compensation schemes, and legal recourse.
Final Recommendations
Based on our analysis of the top brokers and current market conditions:
- For Cost-Conscious Traders: IC Markets offers the lowest spreads (from 0.02 pips) with $3.50 commissions
- For Technology Enthusiasts: Pepperstone’s Smart Trader Tools and multi-jurisdictional regulation provide excellent value
- For Beginners: FXTM combines competitive pricing with comprehensive education and strong regulation
- For High-Leverage Trading: Exness offers unlimited leverage with instant withdrawals for qualified traders
Remember to test any broker thoroughly using demo accounts before committing real money. The best brokers welcome this approach because they’re confident in their service quality.
The forex brokerage industry continues evolving with AI integration, enhanced regulations, and improved technology. By understanding how brokers work and choosing wisely, you’re positioning yourself for long-term trading success in the world’s most liquid market.
Disclaimer
Trading forex carries substantial risk and may not be suitable for all investors. The high degree of leverage can work against you as well as for you. Before deciding to trade forex, you should carefully consider your investment objectives, level of experience, and risk appetite. The possibility exists that you could sustain a loss of some or all of your initial investment and therefore you should not invest money that you cannot afford to lose. You should be aware of all the risks associated with forex trading and seek advice from an independent financial advisor if you have any doubts. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
