Key Takeaways
- South Africa operates under a Twin Peaks regulatory model with FSCA handling market conduct and the Prudential Authority managing prudential supervision
- Forex brokers must obtain FSCA licensing and maintain segregated client funds with maximum leverage of 30:1 for retail traders
- The Financial Stability Oversight Committee (FSOC) coordinates between SARB, FSCA, and PA to ensure financial system stability
- Top FSCA-regulated brokers include AvaTrade, HFM, Exness, and IG Markets with competitive spreads and comprehensive consumer protection
- The regulatory framework prioritizes consumer protection through mandatory fund segregation, transparent pricing, and robust complaint resolution mechanisms
Introduction to South Africa’s Financial Regulatory Framework
Honestly, picking a regulated forex broker in South Africa isn’t rocket science—but understanding the regulatory landscape definitely helps you make smarter choices. If you’ve ever wondered why some brokers seem rock-solid while others disappear overnight, the answer often lies in their regulatory oversight.
South Africa’s financial regulatory framework underwent a massive transformation in 2018 with the implementation of the Twin Peaks model. This system, borrowed from Australia and the Netherlands, fundamentally changed how financial institutions are supervised and has significant implications for forex traders and brokers operating in the region.

The Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) now serves as the market conduct regulator, working alongside the Prudential Authority within the South African Reserve Bank to create a comprehensive supervisory framework. This dual-regulator approach aims to enhance consumer protection while maintaining financial stability—two goals that directly impact your trading experience and fund security.
Background on Financial Regulation in South Africa
Development of Financial Supervisory Frameworks
South Africa’s journey toward modern financial regulation began long before the 2018 Twin Peaks implementation. The country recognized early that its relatively small but highly interconnected financial system needed robust oversight to prevent systemic risks and protect consumers.
Prior to 2018, South Africa operated under a more fragmented regulatory structure. The Financial Services Board (FSB) handled most non-banking financial services, while the South African Reserve Bank supervised banks directly. This system worked reasonably well but had gaps—particularly around coordination and consumer protection.
Pre-2017 Regulatory Framework Challenges
The old system faced several challenges that ultimately led to reform:
- Regulatory silos: Different regulators often worked in isolation, creating coordination problems
- Consumer protection gaps: Market conduct oversight wasn’t sufficiently integrated across all financial services
- Systemic risk blind spots: No single entity had a comprehensive view of system-wide risks
- International standards alignment: The framework needed updating to meet evolving global regulatory standards
Key Regulatory Legislation and Acts
The Financial Sector Regulation Act
The Financial Sector Regulation Act 9 of 2017 serves as the backbone of South Africa’s current regulatory framework. This comprehensive legislation established the Twin Peaks model and created the institutional architecture that governs financial services today.
The Act’s primary objectives include:
- Establishing a system of financial regulation through the Twin Peaks model
- Creating the Prudential Authority within SARB
- Transforming the FSB into the more powerful FSCA
- Defining cooperation mechanisms between regulators
- Enhancing consumer protection measures
Twin Peaks Model Implementation
Cabinet approved the move toward Twin Peaks in June 2011, but implementation took several years of careful planning. The model officially launched on April 1, 2018, marking a watershed moment for South African financial regulation.
As SARB explains, the Twin Peaks model separates prudential regulation (focused on institutional safety and soundness) from market conduct regulation (focused on how institutions treat customers). This separation allows each regulator to develop specialized expertise while maintaining coordination on system-wide issues.
FSCA’s Core Responsibilities in Financial Supervision
Market Conduct Regulation and Consumer Protection
The FSCA’s mission is straightforward: “To ensure a fair and stable financial market, where consumers are informed and protected, and where those that jeopardize the financial well-being of consumers are held accountable.”
This isn’t just regulatory speak—it translates into concrete actions that affect your daily trading experience. When you see a forex broker advertising “FSCA regulated,” they’re signaling compliance with a comprehensive framework designed to protect your interests.
Overseeing Financial Institutions and Markets
The FSCA regulates a broad spectrum of financial service providers, including:
- Forex brokers operating as Financial Service Providers (FSPs)
- Insurance companies and intermediaries
- Collective investment scheme managers
- Credit rating agencies
- Over-the-Counter Derivative Providers (ODPs)
- Market infrastructures and exchanges
Risk Management and Compliance Monitoring
The FSCA doesn’t just set rules and walk away. They actively monitor compliance through:
- Regular inspections: On-site visits to assess compliance with regulatory requirements
- Thematic reviews: Industry-wide examinations of specific risks or practices
- Data collection and analysis: Ongoing monitoring of financial metrics and customer complaints
- Supervisory meetings: Regular dialogue with senior management of regulated entities
For forex brokers, this means the FSCA tracks everything from client fund segregation to marketing practices. They’re particularly focused on ensuring brokers don’t engage in practices that could harm retail traders—like stop-loss hunting or unfair slippage.
Consumer Protection and Market Stability Measures
Fair Treatment Principles
The FSCA operates under six core principles for the fair treatment of customers:
- Fair culture and governance: Institutions must embed fair treatment into their corporate culture
- Product design and pricing: Products must be designed with customer interests in mind
- Clear and fair communication: Information must be clear, accurate, and not misleading
- Suitable advice and sales: Recommendations must be appropriate for the customer’s circumstances
- Performance and service: Services must meet reasonable customer expectations
- Complaint handling: Fair and efficient resolution of customer complaints
These principles aren’t abstract ideals—they translate into specific requirements for forex brokers. For example, brokers must provide clear risk warnings, offer appropriate leverage levels, and maintain robust complaint resolution procedures.
Enforcement and Penalties
The FSCA has significant enforcement powers when brokers step out of line. According to their 2024/25 Regulatory Actions Report, the authority imposed over R119.8 million in administrative penalties across 51 cases.
Common enforcement actions include:
- Administrative penalties: Financial sanctions for regulatory breaches
- License suspension or revocation: For serious or repeated violations
- Public warnings: Alerts about unlicensed or problematic entities
- Enforceable undertakings: Formal agreements to change business practices
Structure and Functions of South African Financial Supervision
The Twin Peaks Architecture
Understanding South Africa’s Twin Peaks model is crucial for grasping how financial supervision actually works. Unlike the mythical “CFSSA,” the real coordination happens through well-defined institutional relationships and formal cooperation mechanisms.
Governance Framework and Coordination Bodies
The Financial Stability Oversight Committee (FSOC) serves as the primary coordination mechanism between South Africa’s financial regulators. This statutory committee includes:
- The SARB Governor (Chairperson)
- Deputy Governor responsible for financial stability
- CEO of the Prudential Authority
- Commissioner of the FSCA
- CEO of the Financial Intelligence Centre (FIC)
- CEO of the National Credit Regulator (NCR)
The FSOC meets regularly to discuss system-wide risks, coordinate regulatory responses, and ensure information flows effectively between different supervisory authorities. This is where the real “council” function happens—not through a separate CFSSA entity.
Collaboration Between FSCA and Prudential Authority
The FSCA and PA have signed comprehensive Memoranda of Understanding that govern their cooperation. These agreements cover:
- Information sharing protocols: How and when to share supervisory information
- Joint inspections: Coordinated examinations of financial institutions
- Crisis management: Coordinated response to institutional failures or market stress
- Regulatory development: Joint development of standards and regulations
International Cooperation and Standards
Global Regulatory Alignment
South African regulators actively participate in international standard-setting bodies:
- Financial Stability Board (FSB): SARB Governor serves on the FSB’s steering committee
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision: PA participates in prudential standard development
- International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO): FSCA contributes to market conduct standards
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF): All regulators coordinate on anti-money laundering standards
This international engagement ensures South African regulations remain aligned with global best practices—which is why FSCA-regulated brokers often meet high international standards.
FSCA Regulation and Forex Brokers in South Africa
Licensing and Compliance Requirements
Here’s where things get practical for forex traders. Every legitimate forex broker operating in South Africa must navigate a comprehensive licensing process under FSCA oversight.
Financial Service Provider (FSP) Licensing
All forex brokers must obtain an FSP license under the Financial Advisory and Intermediary Services Act (FAIS). This license comes with significant responsibilities:
- Fit and proper requirements: Key personnel must meet competency and integrity standards
- Capital adequacy: Sufficient financial resources to operate safely
- Professional indemnity insurance: Coverage for potential client losses due to professional negligence
- Client fund segregation: Keeping client money separate from operational funds
- Compliance programs: Systems to monitor and ensure ongoing regulatory compliance
Over-the-Counter Derivative Provider (ODP) License
Since 2019, forex brokers offering CFDs and other derivatives must also obtain ODP authorization. This additional layer of regulation specifically addresses:
- Leverage limits: Maximum 30:1 leverage for major currency pairs (retail clients)
- Risk warnings: Mandatory disclosure of CFD trading risks
- Client categorization: Different rules for retail vs. professional clients
- Negative balance protection: Preventing client losses beyond account balance
Impact of FSCA Regulations on the Forex Industry
Leverage Restrictions and Consumer Protection
The FSCA’s 30:1 leverage limit for retail traders aligns with European ESMA regulations and represents a significant consumer protection measure. As DailyForex notes, this restriction applies to major currency pairs, with even lower limits for more volatile instruments:
- Major currency pairs: 30:1 maximum leverage
- Non-major currency pairs and gold: 20:1 maximum leverage
- Commodities (excluding gold): 10:1 maximum leverage
- Individual equities and other reference values: 5:1 maximum leverage
Professional clients who meet specific criteria (including minimum net worth requirements) can access higher leverage levels, but most retail traders are protected by these limits.
Client Fund Protection Measures
FSCA regulations require brokers to maintain strict segregation of client funds. As IG South Africa explains, “Your money is held in segregated client bank (independent trust) accounts at registered banks. Your money is never merged with IG’s own money.”
This segregation means:
- Client funds are held in separate accounts at approved banks
- These funds can’t be used for the broker’s operational expenses
- In case of broker insolvency, client funds are protected from creditors
- Regular reconciliation ensures all client money is properly accounted for
Top FSCA-Regulated Forex Brokers
Based on comprehensive market research, here are the leading FSCA-regulated forex brokers available to South African traders:
| Broker | FSP License | Min Spread (EUR/USD) | Leverage (Retail) | Platforms | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AvaTrade | 45984 | 1.3 pips | 30:1 | MT4, MT5, AvaOptions | Copy trading, educational resources |
| HFM | 46632 | 1.2 pips | 30:1 | MT4, MT5, HFM App | Competitive spreads, multiple regulators |
| Exness | 51024 | 1.0 pips | 30:1 | MT4, MT5, Exness App | Instant withdrawals, tight spreads |
| IG Markets | 41393 | 0.6 pips | 30:1 | MT4, IG Platform | Market leader, extensive research |
| FxPro | 45052 | 1.4 pips | 30:1 | MT4, MT5, cTrader | No dealing desk, institutional liquidity |
| FXTM | 46614 | 1.3 pips | 30:1 | MT4, MT5 | Educational focus, local support |
| Tickmill | 49464 | 0.0 pips (Raw) | 30:1 | MT4, MT5 | Raw spreads, low commissions |
| ATFX | 44816 | 1.2 pips | 30:1 | MT5 | Low fees, segregated accounts |
| JustMarkets | 51114 | 1.1 pips | 30:1 | MT4, MT5 | ZAR accounts, local support |
| CM Trading | 38782 | 1.5 pips | 30:1 | MT4, WebTrader | Local South African broker |
Detailed Broker Profiles
AvaTrade – Best Overall FSCA-Regulated Broker

AvaTrade stands out as the top choice for South African traders, holding FSCA license 45984. The broker offers multiple asset classes including forex, stocks, commodities, and cryptocurrencies through various platforms including MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and their proprietary AvaOptions platform.
Key advantages include:
- Multiple regulatory jurisdictions (FSCA, ASIC, FSA)
- Comprehensive educational resources
- Copy trading capabilities
- Competitive spreads starting from 1.3 pips on EUR/USD
HFM – Excellent Multi-Regulated Broker
HFM (formerly HotForex) operates under FSCA license 46632 and provides access to over 1,000 trading instruments. The broker is known for competitive spreads and strong educational support.
Notable features:
- Multiple regulatory licenses (FSCA, CySEC, DFSA, CMA)
- Advanced trading platforms including MT4, MT5, and HFM App
- 24/5 multilingual customer support
- Comprehensive market analysis and educational materials
Exness – Premium Trading Conditions
Exness holds FSP license 51024 and has gained recognition for its instant withdrawal capabilities and competitive trading conditions. The broker recently strengthened its South African presence by obtaining ODP licensing.
Key strengths:
- Instant withdrawals (when using same payment method as deposit)
- Tight spreads from 1.0 pips on major pairs
- Multiple account types including Professional accounts
- Strong technology infrastructure
FXTM – Education-Focused Broker
FXTM (ForexTime) operates under FSP license 46614 and distinguishes itself through comprehensive educational offerings and strong local support for South African traders.
Distinctive features:
- Extensive educational program including webinars and trading courses
- Local South African support team
- Multiple account types for different trading styles
- Strong focus on trader development
Consumer Protection and Dispute Resolution
FSCA’s Consumer Protection Framework
The FSCA takes consumer protection seriously—and as a forex trader, you benefit directly from this focus. The authority’s approach goes beyond just setting rules; they actively monitor compliance and take action when brokers step out of line.
Fair Treatment Principles in Practice
Remember those six fair treatment principles we mentioned earlier? Here’s how they translate into real protections for forex traders:
- Clear risk warnings: Brokers must clearly explain that CFD trading involves significant risk of loss
- Appropriate leverage: The 30:1 limit prevents excessive risk-taking by retail traders
- Transparent pricing: All costs, including spreads and commissions, must be clearly disclosed
- Fair execution: Orders must be executed at the best available price without manipulation
- Accessible complaint procedures: Brokers must have efficient systems for handling customer complaints
Ombud Services and Dispute Resolution
FAIS Ombud: Your Safety Net
When things go wrong with your broker, the FAIS Ombud provides free dispute resolution services. This independent office can investigate complaints and order compensation when brokers breach their obligations.
The Ombud handles complaints involving:
- Unfair trading practices
- Misrepresentation of trading conditions
- Failure to execute orders properly
- Inappropriate advice or recommendations
- Problems with withdrawals or fund access
How to File a Complaint
If you have an issue with an FSCA-regulated broker, follow this process:
- First, complain to the broker directly: Give them a chance to resolve the issue through their internal complaints procedure
- Document everything: Keep records of all communications, trading statements, and relevant correspondence
- Wait for the broker’s response: They typically have 6 weeks to investigate and respond
- If unsatisfied, escalate to the FAIS Ombud: File your complaint within 6 months of the broker’s final response
- Cooperate with the investigation: Provide requested documentation and information
Verification and Due Diligence for Traders
How to Verify Broker Registration
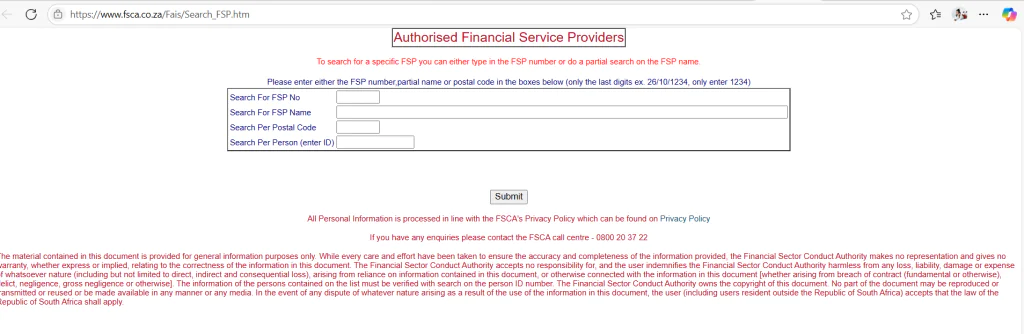
Before opening an account with any broker, always verify their FSCA registration. You can check this through the FSCA’s official register.
Look for:
- Valid FSP license number: This should be prominently displayed on the broker’s website
- Current registration status: Ensure the license is active and not suspended
- Authorized activities: Confirm the broker is authorized for forex/CFD trading
- ODP authorization: For derivative products, ensure they have proper ODP licensing
Compliance and Reporting Obligations
Regulatory Reporting Requirements
FSCA-regulated brokers must maintain extensive reporting to ensure ongoing compliance. This isn’t just bureaucracy—it’s part of the system that protects your funds and ensures fair treatment.
Financial Reporting Standards
Brokers must submit regular financial reports including:
- Monthly client money reconciliations: Ensuring all client funds are properly segregated and accounted for
- Quarterly financial statements: Demonstrating ongoing financial viability
- Annual audited accounts: Independent verification of financial position
- Capital adequacy reporting: Proving they maintain sufficient resources
Operational Compliance Monitoring
The FSCA monitors brokers through various mechanisms:
- Supervisory returns: Regular data submissions on trading volumes, client numbers, and complaint statistics
- On-site inspections: Detailed examinations of business practices and compliance systems
- Thematic reviews: Industry-wide assessments of specific risks or practices
- Mystery shopping: Testing how brokers treat potential clients
Enforcement Actions and Penalties
Recent Enforcement Trends
The FSCA’s approach to enforcement has evolved significantly. According to recent reports, the authority imposed R119.8 million in penalties during 2024/25, demonstrating active supervision.
Common enforcement actions include:
- Administrative penalties: Financial sanctions for regulatory breaches
- License conditions: Restrictions on business activities until compliance is achieved
- Public warnings: Alerts about unlicensed entities or problematic practices
- License revocation: Ultimate sanction for serious or repeated violations
Impact on Broker Operations
These enforcement actions create strong incentives for compliance. Brokers know that regulatory breaches can result in significant financial penalties and reputational damage, encouraging them to maintain high standards.
For traders, this enforcement framework provides confidence that:
- Brokers are actively supervised, not just licensed and forgotten
- Non-compliance carries real consequences
- The regulatory system adapts to address emerging risks
- Consumer protection remains a priority
South Africa’s Twin Peaks Model vs. Other Regulatory Approaches
Comparison with Global Regulatory Models
Twin Peaks vs. Integrated Supervision
Many countries use integrated supervisors (like the UK’s former FSA) where one regulator handles both prudential and conduct supervision. South Africa chose the Twin Peaks approach for specific reasons:
- Specialization benefits: Each regulator can develop deep expertise in their area
- Clearer accountability: Consumers know exactly which regulator handles their concerns
- Reduced conflicts of interest: Prudential and conduct objectives sometimes conflict
- Better crisis management: Specialized teams can respond more effectively to different types of problems
Learning from International Experience
South Africa studied Twin Peaks implementations in Australia and the Netherlands before adopting the model. Key lessons included:
- Coordination is crucial: The two peaks must work together effectively
- Clear mandate definition: Overlaps and gaps must be minimized
- Industry engagement: Regular dialogue with regulated entities improves outcomes
- Gradual implementation: Phased transitions work better than “big bang” approaches
Unique Features of South Africa’s Implementation
Central Bank Integration
Unlike Australia where both regulators are separate entities, South Africa placed the Prudential Authority within the SARB. This creates unique advantages:
- Direct access to central bank expertise: Monetary policy and prudential supervision are closely linked
- Enhanced crisis response: The central bank can provide emergency liquidity while the PA handles institutional issues
- Systemic risk oversight: Better integration of macroprudential and microprudential supervision
- Cost efficiency: Shared resources and infrastructure
Coordination Mechanisms
South Africa developed sophisticated coordination mechanisms that go beyond what exists in other Twin Peaks jurisdictions:
- Financial Stability Oversight Committee: Regular senior-level coordination
- Comprehensive MOUs: Detailed cooperation agreements between regulators
- Joint standards development: Collaborative approach to regulatory development
- Information sharing protocols: Systematic exchange of supervisory information
Benefits and Limitations
Demonstrated Benefits
Since implementation in 2018, the Twin Peaks model has delivered several clear benefits:
- Enhanced consumer protection: More focused attention on market conduct issues
- Improved crisis response: Coordinated handling of COVID-19 impact demonstrated system effectiveness
- Clearer regulatory objectives: Industry understands what each regulator expects
- International recognition: South Africa’s framework is recognized as meeting international standards
Ongoing Challenges
No regulatory system is perfect, and Twin Peaks faces ongoing challenges:
- Coordination complexity: Two regulators require more coordination than one
- Industry adaptation: Firms must manage relationships with multiple regulators
- Resource requirements: Maintaining two specialized regulators is potentially more expensive
- Regulatory arbitrage risks: Firms might try to exploit differences between regulators
Impact of Regulatory Framework on South African Financial Markets
Market Stability and Investor Confidence
The Twin Peaks regulatory framework has demonstrably improved market confidence in South Africa’s financial sector. International assessments, including the IMF’s Financial Sector Assessment Program, have recognized the strength of the current regulatory approach.
Enhanced Market Integrity
The FSCA’s market conduct focus has led to:
- Reduced market manipulation: Active monitoring and enforcement of fair trading practices
- Improved disclosure standards: Better information flow to investors and traders
- Enhanced complaint resolution: More effective mechanisms for addressing trader grievances
- Stronger investor protection: Comprehensive safeguards for retail investors
International Recognition
South Africa’s regulatory framework now ranks favorably in international comparisons:
- FSB peer reviews: Recognition as meeting international standards
- FATF assessments: Strong anti-money laundering framework
- IOSCO evaluations: Effective securities market regulation
- Basel compliance: Strong prudential supervision of banks
Effects on Forex Industry Development
Market Growth and Competition
Robust regulation has actually encouraged forex market development in South Africa:
- Increased broker participation: More international brokers seeking FSCA licenses
- Enhanced product innovation: Regulatory clarity allows for safe product development
- Improved pricing competition: Transparent regulations level the playing field
- Higher professional standards: Better-trained and more competent market participants
Technology and Innovation
The regulatory framework supports technological innovation while maintaining consumer protection:
- Fintech integration: Clear rules for new technology adoption
- Digital platform development: Support for advanced trading platforms
- Mobile trading growth: Regulatory support for smartphone-based trading
- API and algorithmic trading: Framework for automated trading systems
South African Forex Market Growth (2018-2024)
Challenges and Areas for Improvement
Regulatory Innovation Balance
While the current framework is strong, ongoing challenges include:
- Cryptocurrency regulation: Developing appropriate oversight for digital assets
- Cross-border coordination: Managing international regulatory arbitrage
- Technology adaptation: Keeping pace with rapidly evolving trading technology
- Small broker support: Ensuring compliance requirements don’t exclude smaller players
Future Regulatory Priorities
The FSCA’s 2025-2028 Strategy identifies key focus areas:
- Digital transformation: Adapting supervision to digital-first business models
- Sustainable finance: Integrating climate and ESG considerations
- Financial inclusion: Ensuring regulatory requirements don’t exclude underserved populations
- International cooperation: Strengthening cross-border regulatory coordination
Future of Financial Supervision in South Africa
Emerging Challenges and Opportunities
Digital Economy Integration
The rapid digitization of financial services presents both opportunities and challenges for South African regulators. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated adoption of digital trading platforms, creating new supervisory considerations.
Key developments include:
- Mobile-first trading platforms: Increasing numbers of traders using smartphones as their primary trading device
- AI and algorithmic trading: Growing use of artificial intelligence in trading decisions and risk management
- Social trading platforms: Copy trading and social investment networks gaining popularity
- Robo-advisors: Automated investment advice platforms entering the market
Regulatory Technology (RegTech) Adoption
Both regulators and regulated entities are increasingly using technology to improve compliance and supervision:
- Automated reporting: Real-time data submission replacing periodic manual reports
- Predictive analytics: Using data science to identify potential problems before they occur
- Digital compliance monitoring: Continuous monitoring of broker activities
- Blockchain applications: Exploring distributed ledger technology for regulatory reporting
Regulatory Evolution and Adaptation
Emerging Risk Management
The regulatory framework continues evolving to address new risks:
- Cyber security requirements: Enhanced protection for client data and trading systems
- Climate risk integration: Considering environmental factors in financial stability assessment
- Operational resilience: Ensuring brokers can continue operating during disruptions
- Third-party risk management: Oversight of outsourcing and technology dependencies
International Coordination Enhancement
Cross-border coordination becomes increasingly important as markets globalize:
- Regulatory sandboxes: Coordinated testing environments for financial innovation
- Mutual recognition agreements: Streamlined authorization for international brokers
- Information sharing enhancement: Real-time sharing of supervisory information
- Joint enforcement actions: Coordinated responses to cross-border violations
Implications for Forex Traders
Enhanced Protection Measures
Future regulatory developments will likely provide even stronger trader protections:
- Real-time monitoring: Immediate detection of problematic broker behavior
- Enhanced compensation schemes: Better protection for client funds in case of broker failure
- Improved dispute resolution: Faster and more effective complaint handling
- Advanced risk warnings: More sophisticated disclosure of trading risks
Technology-Enabled Trading
Regulatory support for innovation will benefit traders through:
- Better trading platforms: More sophisticated and user-friendly interfaces
- Lower costs: Technology-driven efficiency reducing trading costs
- Enhanced analytics: Better market analysis and trading tools
- Improved execution: Faster and more accurate order processing
Conclusion
Summary of South Africa’s Financial Regulatory Excellence
South Africa’s financial regulatory framework represents a sophisticated and effective approach to financial supervision. While the mythical “Council for Financial Supervisors of South Africa (CFSSA)” doesn’t exist, the actual coordination mechanisms—particularly the Financial Stability Oversight Committee (FSOC)—provide robust oversight and coordination between regulatory authorities.
The Twin Peaks model has demonstrated clear benefits since its 2018 implementation:
- Enhanced consumer protection: The FSCA’s focused mandate has strengthened trader protections
- Improved market integrity: More effective supervision of market conduct
- Better crisis response: Coordinated regulatory response during COVID-19 demonstrated system resilience
- International recognition: South Africa’s framework meets global regulatory standards
Key Recommendations for Forex Traders
Based on this comprehensive analysis, here are essential recommendations for South African forex traders:
- Always verify FSCA registration: Use the official FSCA register to confirm broker licensing
- Understand leverage limits: The 30:1 limit protects you from excessive risk
- Confirm fund segregation: Ensure your broker properly segregates client funds
- Know your rights: Understand complaint procedures and ombud services
- Stay informed: Keep up with regulatory developments that affect your trading
Future Outlook for South African Financial Regulation
The regulatory framework will continue evolving to address emerging challenges while maintaining its core strengths. Key trends include greater use of technology in supervision, enhanced international cooperation, and continued focus on consumer protection.
For forex traders, this evolution promises even better protection, more innovative products, and more competitive pricing. The strong regulatory foundation provides confidence that South Africa will remain an attractive destination for both international brokers and local traders.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the CFSSA and what role does it play in South Africa’s financial sector?
- The “Council for Financial Supervisors of South Africa (CFSSA)” doesn’t exist as a formal regulatory entity. Financial supervision coordination happens through the Financial Stability Oversight Committee (FSOC), which includes representatives from SARB, FSCA, PA, FIC, and NCR. This committee serves as the primary forum for regulatory coordination and information sharing.
- What is the primary role of financial supervisors in South Africa?
- South Africa’s financial supervisors operate under the Twin Peaks model: the FSCA focuses on market conduct and consumer protection, while the Prudential Authority (within SARB) handles prudential supervision of financial institutions. The SARB maintains overall financial stability and monetary policy responsibilities.
- Which institutions are regulated by FSCA?
- The FSCA regulates forex brokers (as FSPs and ODPs), insurance companies, collective investment schemes, credit rating agencies, market infrastructures, and other financial service providers. All legitimate forex brokers in South Africa must hold FSCA licenses.
- How does FSCA ensure compliance among forex brokers?
- The FSCA uses multiple supervisory tools including regular reporting requirements, on-site inspections, thematic reviews, mystery shopping exercises, and enforcement actions. In 2024/25, they imposed over R119.8 million in penalties across 51 enforcement cases.
- What is the Financial Sector Regulation Act, and how does it impact regulatory oversight?
- The Financial Sector Regulation Act 9 of 2017 established South Africa’s Twin Peaks regulatory model, created the FSCA and PA, and defined their respective mandates. It provides the legal framework for modern financial supervision and enhanced consumer protection.
- How does the Twin Peaks model work in South Africa?
- The Twin Peaks model separates prudential regulation (PA focuses on institutional safety) from market conduct regulation (FSCA focuses on consumer protection). This specialization allows each regulator to develop expertise while coordination mechanisms ensure they work together effectively.
- How do financial supervisors protect investors in the forex market?
- Protection measures include mandatory client fund segregation, leverage limits (30:1 for retail traders), negative balance protection, transparent pricing requirements, comprehensive risk warnings, and access to the FAIS Ombud for dispute resolution.
- Are forex brokers required to be licensed by FSCA?
- Yes, all forex brokers operating in South Africa must hold FSP licenses under FAIS. Since 2019, they also need ODP (Over-the-Counter Derivative Provider) authorization to offer CFDs and other derivative products.
- How can investors verify if a broker complies with FSCA regulations?
- Check the FSCA’s official register at www.fsca.co.za to verify FSP license numbers and registration status. Look for current licenses, authorized activities, and any enforcement actions or conditions.
- What penalties exist for non-compliance with FSCA regulations?
- Penalties include administrative fines, license suspension or revocation, public warnings, enforceable undertakings, and criminal prosecution for serious violations. The FSCA imposed over R119.8 million in penalties during 2024/25.
- How does FSCA differ from other financial regulators in South Africa?
- The FSCA focuses specifically on market conduct and consumer protection, while the Prudential Authority handles institutional safety and soundness. SARB maintains overall financial stability and monetary policy. Each has distinct but complementary roles.
- What are the key responsibilities of the FSCA?
- Key responsibilities include licensing and supervising financial service providers, enforcing market conduct standards, protecting consumers, maintaining market integrity, handling complaints, and cooperating with other regulators on financial stability.
- How does the regulatory framework protect consumers?
- Consumer protection includes the six fair treatment principles, mandatory client fund segregation, leverage limits, transparent pricing, clear risk warnings, accessible complaint procedures, and the FAIS Ombud for dispute resolution.
- What is the relationship between SARB and financial supervisors?
- SARB houses the Prudential Authority and maintains overall financial stability responsibility. It coordinates with the FSCA through the Financial Stability Oversight Committee and various MOUs. SARB also handles monetary policy and payment system oversight.
- Can financial regulators revoke a broker’s license?
- Yes, the FSCA can suspend or revoke FSP licenses for serious violations, repeated non-compliance, or when brokers no longer meet licensing requirements. This is the ultimate enforcement sanction for protecting consumers.
- What are the advantages of choosing FSCA-regulated brokers?
- Advantages include segregated client funds, leverage protection, transparent pricing, professional standards compliance, access to dispute resolution, regulatory oversight, and protection under South African law.
- How does the Twin Peaks model enhance financial stability?
- By separating prudential and conduct supervision, each regulator can specialize while coordination mechanisms ensure comprehensive oversight. This reduces regulatory gaps and conflicts of interest while improving crisis response capabilities.
- What is an ODP license and why is it important for forex trading?
- An Over-the-Counter Derivative Provider license is required for brokers offering CFDs, forex, and other derivatives. It ensures compliance with specific product rules including leverage limits, risk warnings, and client categorization.
- How do leverage limits protect retail traders?
- The 30:1 leverage limit for major currency pairs prevents excessive risk-taking by retail traders, reducing the likelihood of catastrophic losses while still allowing reasonable profit opportunities.
- What should traders do if they have a complaint against a broker?
- First complain directly to the broker through their internal procedures. If unsatisfied, escalate to the FAIS Ombud within 6 months. Document all communications and cooperate with investigations.
- How does international coordination benefit South African traders?
- International coordination ensures South African regulations meet global standards, facilitates market access for reputable international brokers, enables information sharing on cross-border risks, and supports joint enforcement actions.
- What role does technology play in modern financial supervision?
- Technology enables real-time monitoring, automated reporting, predictive analytics for risk detection, digital compliance systems, and more efficient supervisory processes, ultimately benefiting trader protection and market integrity.
- How has the regulatory framework evolved since 2018?
- Evolution includes implementation of ODP licensing for derivatives, enhanced enforcement capabilities, improved international coordination, adoption of regulatory technology, and ongoing adaptation to digital transformation in financial services.
- What are the current challenges facing South African financial regulation?
- Current challenges include cryptocurrency regulation, cross-border coordination, technology adaptation, balancing innovation with consumer protection, and ensuring regulations don’t exclude smaller market participants.
- How do regulators coordinate during financial crises?
- Coordination happens through the Financial Stability Oversight Committee, established MOUs, joint crisis management protocols, information sharing agreements, and regular communication between regulatory authorities.
- What future developments can traders expect in South African regulation?
- Expected developments include enhanced digital supervision, improved technology integration, stronger international cooperation, better consumer protection measures, and continued adaptation to evolving market structures.
- How does South Africa’s regulatory framework compare internationally?
- South Africa’s Twin Peaks model is recognized internationally as meeting global standards, with the IMF and other bodies acknowledging the strength of the current regulatory framework and its effective implementation.
- What resources are available for traders to stay informed about regulations?
- Resources include the FSCA website, regulatory newsletters, industry publications, broker communications, professional associations, and financial education initiatives provided by regulators and industry bodies.
- How do fund segregation requirements protect traders?
- Segregation requirements ensure client funds are held separately from broker operational funds in designated trust accounts at approved banks, protecting these funds from creditors if the broker fails.
- What is the significance of South Africa’s regulatory recognition internationally?
- International recognition facilitates cross-border business, attracts reputable international brokers, supports mutual recognition agreements, enhances market confidence, and demonstrates regulatory quality to global investors.
Disclaimer
Trading forex carries substantial risk and may not be suitable for all investors. The high degree of leverage can work against you as well as for you. Before deciding to trade forex, you should carefully consider your investment objectives, level of experience, and risk appetite. The possibility exists that you could sustain a loss of some or all of your initial investment and therefore you should not invest money that you cannot afford to lose. You should be aware of all the risks associated with forex trading and seek advice from an independent financial advisor if you have any doubts. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
